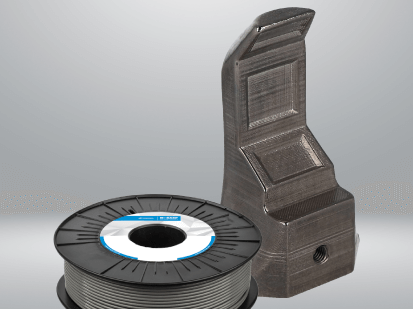
Thank you for choosing BASF Forward AM Metal Filaments
Let's Get You Started with Metal 3D Printing!
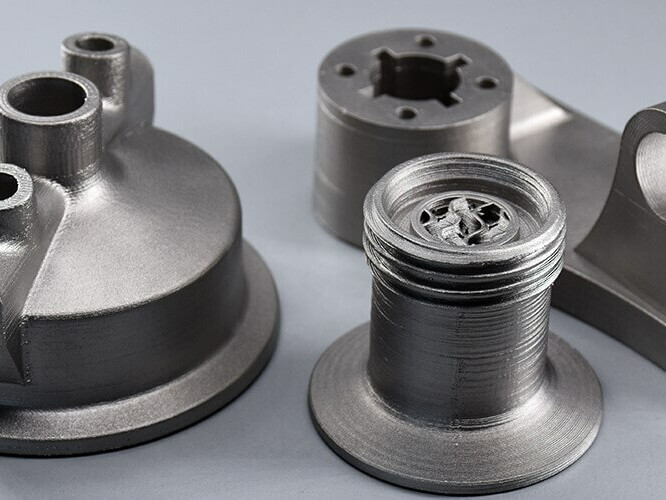
FFF Printed Metal
Printing Ultrafuse® Metal Filaments Step by Step
This Quick-Start Guideline on the use of BASF Ultrafuse® 316L and BASF Ultrafuse® 17-4 PH will help you make the most out of your metal printing project and cover the most important steps of 3D modeling, preparing models on your 3D printer, as well as preparing 3D prints for post-processing.
PRINTING
Following our Print Preparation Checklist, Recommended Printer Parameters, and 3D Modelling Guideline ensures your FFF printer extrudes Ultrafuse® Metal Filament and Support Layer correctly.
GREEN PART

3D prints made with BASF Ultrafuse® 316L and BASF Ultrafuse® 17-4 PH are called “green parts” and contain metallic powder and polymeric filler.
DEBINDING

Debinding, a key post-processing step in metal printing, removes binder material before sintering, preventing deformation and increasing sintering efficiency.
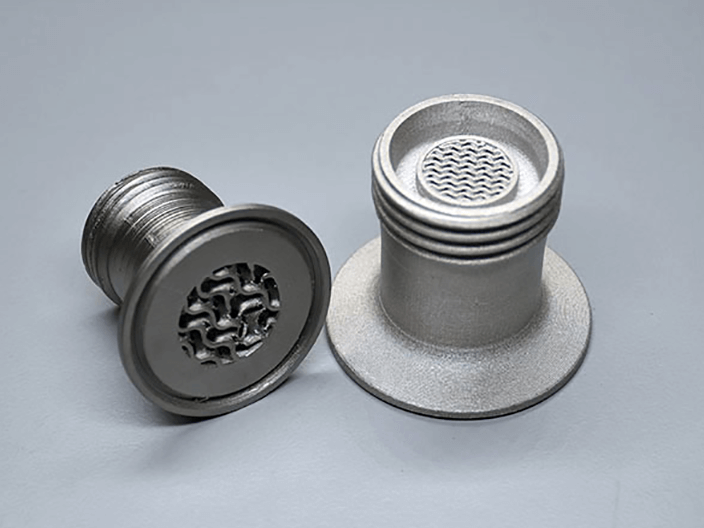
BROWN PART

After the first stage of post-processing, debinding, these prints are called "brown parts" and no longer contain the polymer filler.
SINTERING

The final step is to sinter, resulting in a 'white part' made entirely of metal.
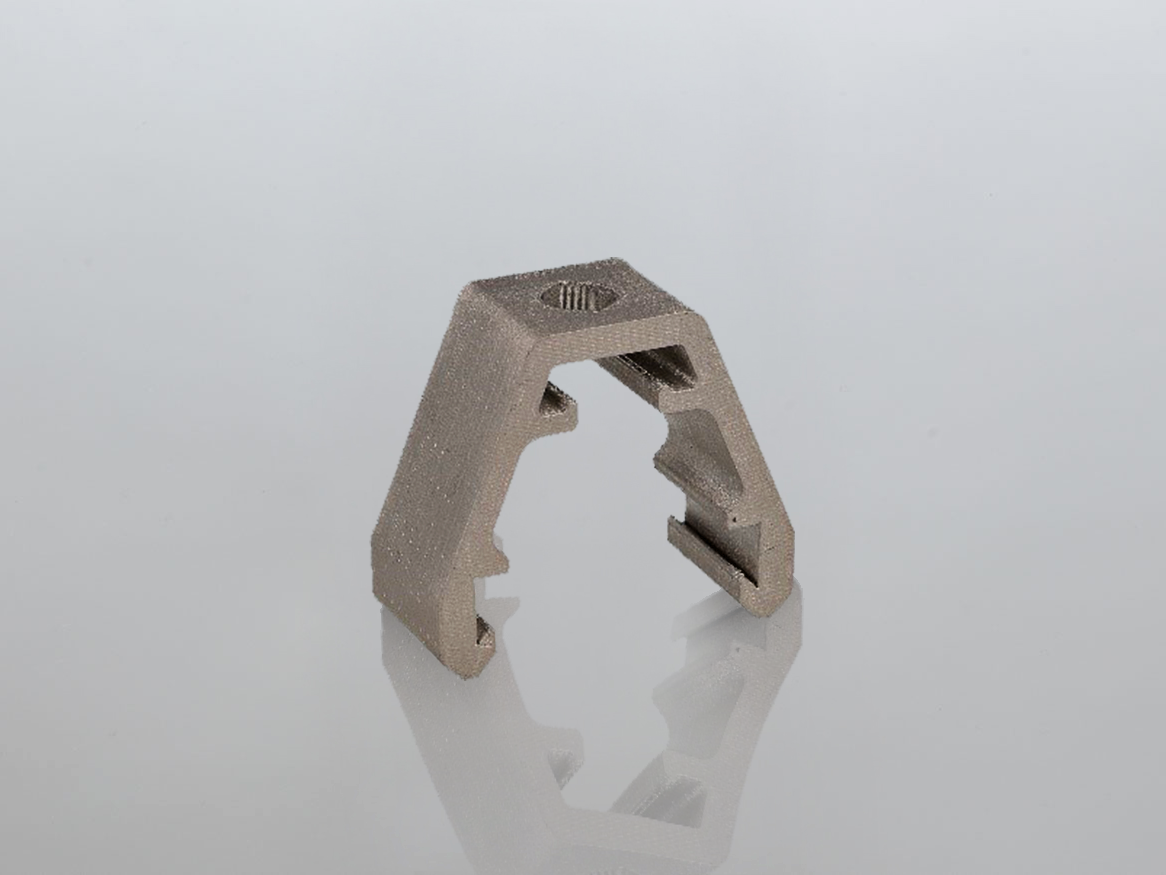
METAL PART

With your all-metal 'white part' in hand, you can carry out all the post-processing steps you would with any metal part produced by conventional methods.
Print-Preparation Checklist
- Ultrafuse® 316L or 17-4 PH Metal Filament matching properties of your desired application
- Ultrafuse® Support Layer required to facilitate the separation of support from the metal part during the final sintering post-processing step
- D&S Voucher required for Debinding and Sintering (D&S), handled by an external service provider through our D&S Portal
- Hardened Nozzle made of hardened steel for lasting high-quality prints
- Approved Glues to dramatically reduce first layer separation and warpage at the build surfaces. Adhesives such as Magigoo Pro Metal or Dimafix are highly recommended.
- 3D-Modell with a maximum dimension of 100 mm x 100 mm x 100 mm complying with the 3D Modelling Guideline below
Printer Requirements
It is possible to print Ultrafuse® metal filaments with a standard desktop FFF printer, however; the chosen machine and its condition can dramatically influence part accuracy and quality. Similar to traditional FFF materials like ABS, warpage can occur with temperature variations and it is therefore recommended to fully enclose the printing chamber to limit air flow. Printing stability can in some situations benefit from actively heated chambers but are not essential.
Ultrafuse® metal filament causes more nozzle wear than traditional plastic filaments due to its high metal content. Hardened nozzles last longer, but regular brass nozzles can work well if replaced frequently. Replace non-hardened nozzles after every 3kg of filament. Always use new, clean nozzles for Ultrafuse® to avoid hazards to printed parts and debinding/sintering equipment.
At 3 kg (6.6lbs) supplying material from a full spool can be difficult for some printers and can result in under extrusion and other flow issues. Therefore, a spool holder using bearings or other techniques of reducing the required force to deploy filament is recommended. Any number of DIY or commercial options, like the Polymaker PolyBox, have been proven effective.
Ultrafuse® Metal Filaments and the Ultrafuse® Support Layer are supported with leading FFF printers to achieve the best printing performance. The complete overview of supported printers can be found in here: Print Profiles for Ultrafuse® Filaments
Use the following links to download the latest print profile at the machine manufacturers website of your FFF 3D printer.
BASF Ultrafuse® 316L:
Raise 3D
Prusa
BCN3D
Download at Ultimaker.com
BASF Ultrafuse® 17-4 PH:
Raise 3D
Prusa
BCN3D
Download via Ultimaker website
| Nozzle Temperature | 230 – 250 °C / 446 – 482 °F |
| Build Chamber Temperature | – (Fan off) |
| Bed Temperature | 90 – 100 °C / 194 – 212 °F |
| Bed Material | Glass + approved glues* / polyimide tape (*Magigoo® suggested) |
| Nozzle Diameter | ≥ 0.4 mm |
| Print Speed | 15 – 50 mm/s |
| Scaling |
XY 120 % ; Z 124 % |
Material Information
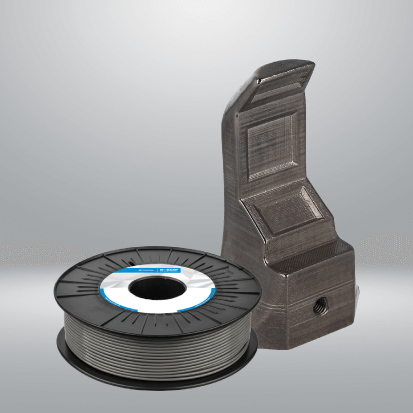
BASF Ultrafuse® 316L stands out as a premier industrial composite filament tailored for leading FFF 3D printers (check out our comprehensive list of compatible printers below). Its cutting-edge features empower users to craft metal components securely, conveniently, and affordably compared to alternatives like Metal Injection Molding, Selective Laser Sintering, or metal machining. This filament boasts a composition of 88% 316L stainless steel particles and 12% polymer content.
Downloads:
- Technical Data Sheets EN, FR, ES, DE, ZH
- User Guidelines
- Debinding Simulation Guidelines
- Process Guidelines
- Safety Data Sheets EN, other languages
BASF Ultrafuse® 316L VS. BASF Ultrafuse® 17-4 PH:
| Type of steel | Corrosion Resistance | Structure | Mechanical performance |
| 316L | Stainless | Non-magnetic | Medium hardness / high elongation |
| 17-4 PH | Corrosive | Magnetic | High hardness / low elongation |
See our Full Comparison Sheet for more support on material choice.
The versatility of BASF Ultrafuse® 316L extends to various applications, including crafting intricate metal end-use parts, functional prototypes, medical devices, automotive components, chemical pipelines or valves, as well as tool or fixture elements. With remarkable tensile strength of up to 561 MPa, yield strength of 251 MPa, and elongation at break of up to 53%, printed parts exhibit an austenitic (non-magnetic) microstructure.
Applications Include:
- Welding-ready parts,
- Tooling, jigs and fixtures.
- Automotive components resistant to corrosion
- Equipment exposed to various chemicals and fluids
- Decorative elements including trims and grilles
- Essential parts within hydraulic systems
- Containers for storing food items
- Medical apparatus and instruments
- Precision mechanisms requiring corrosion resistance
BASF’s Ultrafuse® 17-4 PH is a premium industrial composite filament designed compatible with leading FFF 3D printers. Its advanced properties enable users to produce metal parts easily, safely and cost-effectively, providing a superior alternative to metal injection molding or conventional metal machining. Consisting of 88% 17-4 stainless steel particles and 12% polymer content, this filament delivers exceptional performance.
Available downloads:
- Technical Data Sheets EN, FR, ES, DE, ZH
- User Guidelines
- Process Guidelines
- Safety Data Sheets EN, other languages
BASF Ultrafuse® 17-4 PH VS. BASF Ultrafuse® 316L: See our Full Comparison Sheet for more support on material choice.
The versatility of BASF Ultrafuse® 17-4 PH extends to a wide range of applications, including the production of robust metal end-use parts, functional prototypes, weather resistant elements, medical devices, automotive components, chemical piping or valves, and tooling or jig components. With an impressive tensile strength of up to 1004 MPa, yield strength of 764 MPa and elongation at break of up to 4%, the printed parts have a martensitic (magnetic) microstructure.
Applications Include:
- Functional prototypes,
- Metal end-use parts,
- Elements requiring weather resistance,
- Medical equipment,
- Automotive parts,
- Components for chemical industry,
- Parts intended for welding,
- Customized tooling, jigs, fixtures.
BASF’s Ultrafuse® Support Layer serves as a specialized support filament tailored for metallic powder filaments. Its use is critical to achieving the desired part geometry, ensuring precision during both the 3D printing and post-processing phases*.
Available Downloads:
- Technical Data Sheet: EN, FR, ES, DE
- User Guidelines Support Layer
- Safety Data Sheet: EN, other languages
*Ultrafuse® Support Layer is not available to our customers the USA & CANADA.
For optimal preservation, it’s advisable to store both BASF Ultrafuse® 316L and BASF Ultrafuse® 17-4 PH filaments within temperatures ranging from 15 to 25 °C, preferably in their original packaging. Ensure the storage environment remains clean and dry. Adhering to these recommended storage conditions extends the shelf life of the filaments for up to 12 months.
Design Guidelines
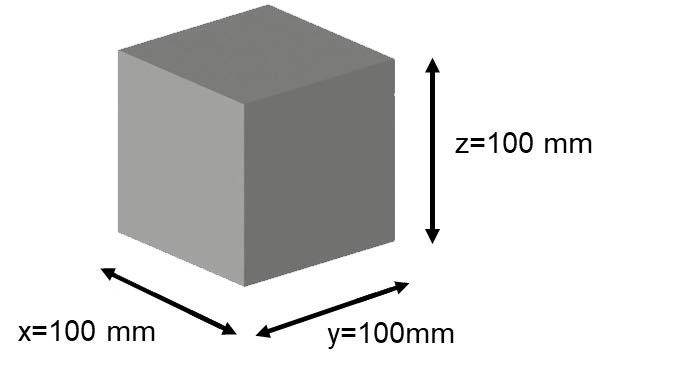
Due to the dimensions of the ceramic plates used to support 3D prints during post-processing, the maximum allowable size for green parts is 100 x 100 x 100 mm (3.93 x 3.93 x 3.93 in). For larger parts, arrangements must be made with the post-processing service provider, although it’s important to acknowledge that larger parts may be susceptible to warping.
For optimal 3D printing outcomes, it is recommended to adhere to measurements of 60 x 60 x 60 mm (2.36 x 2.36 x 2.36 in).
3D printed parts made with BASF Ultrafuse® 316L and BASF Ultrafuse® 17-4 PH experience shrinkage of approximately 20% in the Z-axis and 16% in the X- and Y-axes during post-processing. This phenomenon needs to be taken into account during the 3D modelling phase by scaling the models to compensate for the expected shrinkage.
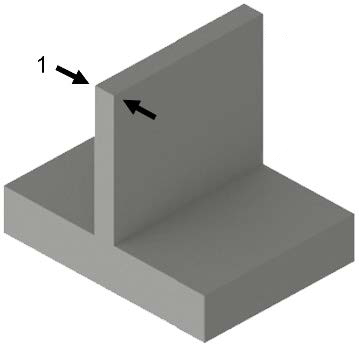
Please be advised that in the planned 3D model, a minimum wall thickness of 1 mm (0.03 in) is required. Walls thinner than this specification (1 mm or 0.03 in) may distort during post-processing.
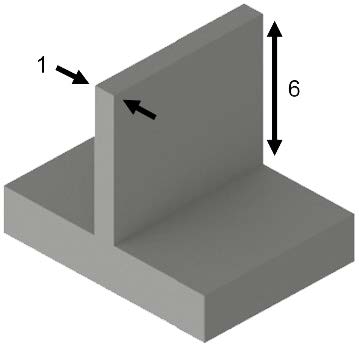
Design unsupported walls with a height-to-width ratio below 6:1 to avoid cracking or collapsing. When using BASF’s Ultrafuse® filaments, use more supports than typical thermoplastics, with angles below 45°. Preferably, design parts to minimize overhangs and the need for extensive supports.
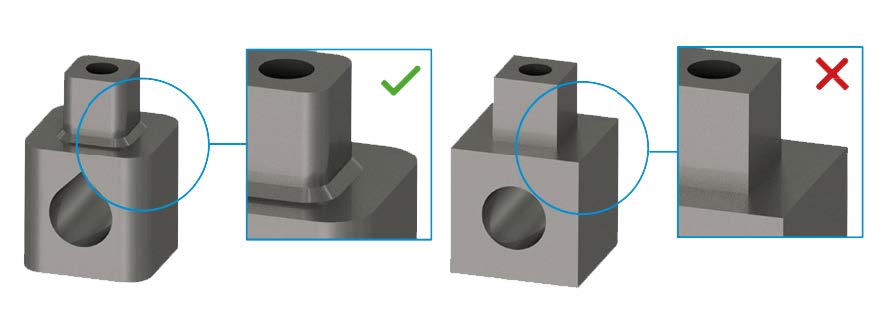
Throughout post-processing, green parts undergo thermal stresses, potentially leading to layer delamination or cracking. Projects featuring notches and sharp edges are particularly susceptible to this layer separation phenomenon. Therefore, incorporating fillets or chamfers into designs is advisable to mitigate such issues.
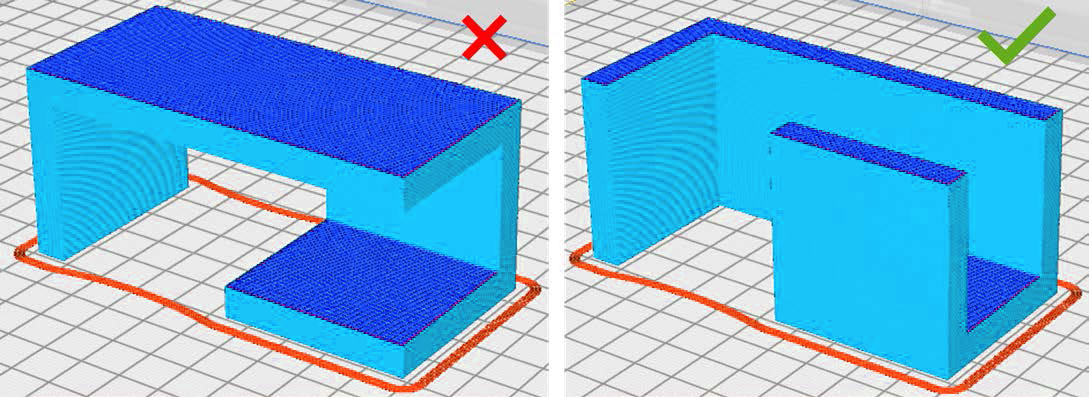
The correct orientation of models on the platform can impact accuracy, durability, and stability throughout the debinding and sintering phases. Therefore, it’s crucial to orient parts in a manner that maximizes contact between the platform and as many flat surfaces as possible.
How to work with the D&S Portal
Take the last steps to receive your final metal part.
After successfully printing your “green part”, it’s time to let our partners handle the next step in debinding and sintering your final metal “white part”. Learn from our explanatory video below on how to work with the Debinding & Sintering Portal on our website to find a local D&S service and book a slot and the guidelines on safe packaging, etc.



Happy with Your Print?Share your Use Case!
Showcase your innovative creations and projects! Share your success stories with us and be featured across BASF Forward AM's social media channels and marketing materials. Additionally, explore collaboration opportunities and receive personalized support from our expert team to take your projects to the next level.
Your Feedback Matters!
Support us by taking our 2 minute survey now and help us to drive innovation and advance our next product generations.