
How Ultrasint® TPU Enables a Recycling Stream
Our previous sustainability articles talked about how Additive Manufacturing can contribute to making a business more sustainable – but what happens after the production? With our Ultrasint® TPU materials, sustainability does not stop after the production process! The 3D printed component material can be used beyond its intended use by recycling the product and using the recycled TPU for other purposes.
Let’s take a look at how this process works in detail and how footwear manufacturer HILOS leverages the sustainable properties of Forward AM’s TPU.
Setting the foundation: Forward AM’s Ultrasint® TPUs
Forward AM provides a versatile TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane Powder) portfolio: Ultrasint® TPU01 for HP MJF 5200, Ultrasint® TPU 88A for SLS printers, and Ultrasint® TPU 88A black that enables printing on SLS desktop machines. The Ultrasint® TPU powders are perfectly suited for parts that require shock absorption, energy return, or flexibility – ideal for applications across industries – such as protective gear, orthotics and prosthetics, footwear and industrial ergonomic applications.
Focusing on the respective AM technology Powder Bed Fusion, it’s being considered quite sustainable, especially when it comes to low and medium-size series. The powder bed of the build chamber in Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) eliminates the need for support structures as the not sintered powder holds each sintered cross-section in place as the build proceeds. With TPU oftentimes being the go-to material for parts with lattice structures, build jobs can show a print volume as low as 6 percent – if that powder was not used it would be an expensive material waste. Aiming at a more sustainable way, we at Forward AM have developed our TPUs convincing with the high reusability rate of up to 80 percent – instead of throwing the material away, it gets reused by adding fresh powder.
Powder for a new printing process is often made up of 80% reused and 20% fresh powder. The reusability of the TPU powder is also not only limited to one cycle but can be reused in multiple print runs, without seeing significant changes in the mechanical properties.
So, the benefits of using TPU and therefore the ability to reuse the power for multiple printing cycles is that almost no powder is being wasted. Making your production not only more sustainable but also more cost-effective. However, a big part of being sustainable is not only the production site but also the recycling aspect as well.
How does a TPU recycling stream work?
It is possible to recycle Ultrasint® TPU 88A and Ultrasint® TPU01. No matter if the part was manufactured by using Selective Laser Sintering or Multi Jet Fusion technology. After the material is recycled, it can be used in injection molding. This recycling workstream is so appealing because the material does not substantially lose any of its mechanical properties through the recycling process.
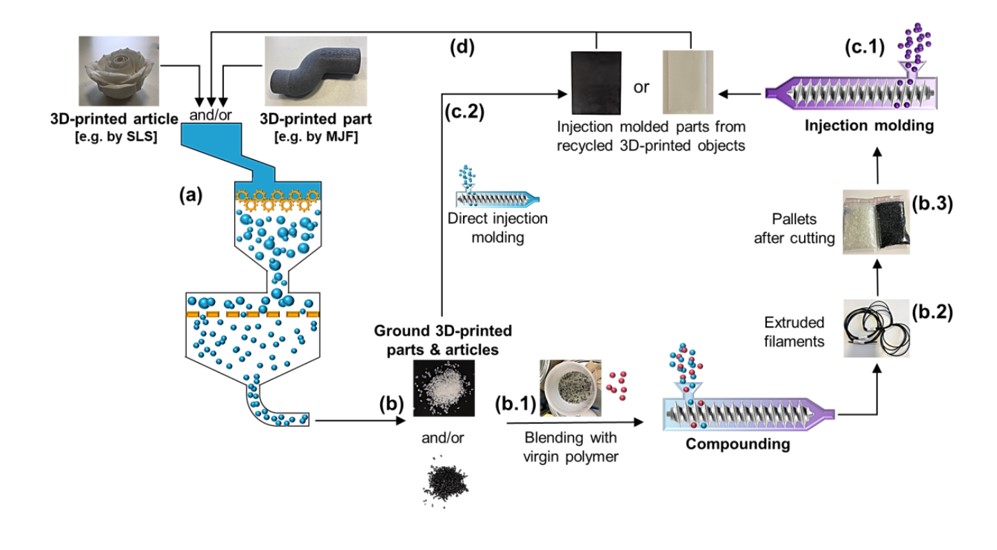
But how exactly does a TPU recycling stream work? The picture below shows that it all starts with a TPU printed part. These parts are then grinded using conventional micronization techniques (a). Through this process, granulate is created (b), which is then blended with virgin TPU (b.1) and, lastly, compounded into a filament (b.2). The last procedure is using extrusion under typical process conditions of TPU compounding. The next step is to cut the filaments to receive pellets (b.3). The pellets are then used as raw materials during injection molding (c.1). An alternative approach can be seen in (c.2). The granulate is not blended with virgin TPU but instead applied directly to manufacture the injection-molded specimen. In the end, step (d) describes the process of recycling molded parts obtained from recycled 3D-printed objects. This shows that this method is for both 3D printed parts and injection molded parts.
HILOS – A sustainable front runner
The American startup HILOS is combining Additive Manufacturing and expert handcraftsmanship to produce unique footwear. An essential element of their vision is to be as sustainable as possible while manufacturing shoes. This is also one of the reasons why they count on Additive Manufacturing: it allows them to only produce a pair of shoes when it has been ordered – reducing waste and overproduction!
HILOS chose Forward AM’s Ultrasint® TPU for two sustainable reasons – its reusability during the print process that allows no material waste as well as the option to recycle the produced parts in the future. Thanks to these material properties, HILOS has been able to advance towards complete product recyclability. According to Forward AM internal studies, this material shows zero degradation post-printing, allowing it to be ground down after use and subsequently utilized for injection molding.
As a result, HILOS offers their customers and partner brands the ability to send shoes back at the end of life, enabling a circular future for footwear.
To further examine their environmental impact, HILOS worked with Yale’s Center for Business and the Environment and HILOS supply chain partners to assess the impact of the 3D printed shoes. The study shows that by using 3D printing, HILOS can save up to 99 percent of water compared to traditional manufacturing and reduce their CO2 emissions by about 48 percent. The tested shoe, the Emmett slip-on mule, needs 89.2 liters of water to be produced, 11.1 kg CO2 is emitted, and 1 gram of glue is used. If you want to read the complete study, click here.
We at Forward AM are here to support you on your way to establishing your recycling stream with our Ultrasint® TPU01! If you have any questions concerning this topic, do not hesitate to contact us.
Share this page
Other Blog Posts
LAYERbyLAYER: A Conversation with Mattia Mucci of Treddy
Welcome to LAYERbyLAYER: Interviews with 3D Printing Services, a unique series brought to you by BASF Forward AM.
Exploring the Future of Injection Molding: A Dual Perspective
In the evolving world of manufacturing, the integration of traditional practices with innovative technologies is not just a trend…
Full Guide: Polyurethane Molds with Ultracur3D® RG 1100 B / xPRO1100-Black
In the rapidly evolving world of product development, speed and flexibility are a must. This is where 3D printed PU molds steps…


